
Get a Quote
Get a Quote and Find Services to Fit Your Needs 50000+ Satisfied Clients
5000+ Licenses & Registration
15 Branches across India
75 Years + Combined experience
This post was originally published in 2023 and has been updated on August 02, 2025, to provide you with the most current and accurate information.
The full form of FEMA is Foreign Exchange Management Act. It is an act that consolidates and amends the laws regarding foreign exchange. The objective of FEMA act 1999 is to facilitate external trade and payments and also, to develop and maintain the foreign exchange market in India.
The act was passed in 1999, and it replaces the Foreign Exchange Regulation Act (FERA) in June 2000. The act was replaced because it did not comply with the post-liberalization policies of the government. And there is much need for this act to change because of the shortage of foreign exchange in the country. Also, under this act, foreign exchange-related issues convert into civil offenses. Check all the FEMA regulations below to know the different aspects, before applying for the FEMA registration.
As stated above the main objective of FEMA act 1999 is to grow and maintain the Indian Forex Market. Other fema objectives are as follows:
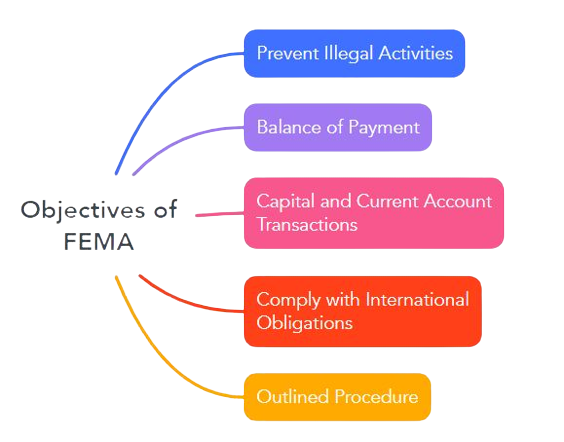
1. Prevent Illegal Activities: FEMA prevents money laundering, financing of terrorism, or unauthorized foreign exchange transaction by providing a legal framework for monitoring, investigation, and enforcement of foreign exchange transactions.
2. Balance of Payment: As per FEMA, the balance of payment is a report that includes transactions of goods, services, and assets between the citizens of various nations. It has two categories; capital account and current account.
3. Capital and Current Account Transactions: The capital account includes investments in securities and immovable property which are subject to certain restrictions and regulations. Current account transactions include trade in goods and services, remittances, and payments are allowed without any restrictions.
4. Comply with International Obligations: FEMA aims to ensure that India’s foreign exchange transactions are consistent with its international obligations and comply with international laws and regulations.
5. Outlined Procedure: FEMA has outlined the process and procedure of all transactions in India which include both the account capital and current transactions.
In India, the primary authority that regulates foreign exchange and FEMA registration is the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). The income tax act is applicable to NRI accounts and company accounts for calculating tax. Companies Act 2013 will apply to all the transactions of the company and SEBI will apply to capital instruments.
Below is the mandatory FEMA compliance checklist for different provisions and rules that are as follows:
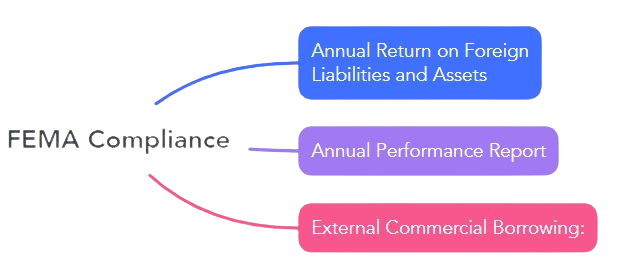
Every Indian resident company that made an FDI in the prior year, including the current year, needs to submit a Foreign Liabilities and Assets (FLA) return. A company is exempt from submitting the FLA if it has no investment holdings. Each year, you must submit this return.
A resident who receives an Overseas Direct Investment (ODI) must submit an annual performance report. Regarding joint ventures or wholly owned subsidiaries outside of India, all of this information must be submitted in Form ODI Part II to the Authorized Dealer Bank by December 31st of each year, at the latest.
Every month all the borrowers have to report all External Commercial Borrowings (ECB) transactions to RBI through an AD Category - I Bank through the Form ‘ECB 2 Return’.
FEMA is applicable all over India, in all branches, offices, and agencies outside India which are owned or controlled by a person who is a resident of India. The headquarters of the FEMA situate in New Delhi, known as Enforcement Directorate. The FEMA is applicable to the following:
The provisions of FEMA provide free transactions on current accounts as per the rules of RBI. Other provisions of the FEMA are as follows:
Any person can sell or withdraw foreign exchange from an authorised dealer, this transaction is free to do if the transaction is in the current account. Some transactions are prohibited like remittance of:
Other than these activities, RBI approval is required to importers for availing of Supplier’s Credit beyond 180 days and buyer’s Credit irrespective of time.
The foreign nationals are not allowed to invest in any business which is related to chit funds, agriculture, plantation, etc. FEMA provisions provide a complete list of permissible classes for an India resident and non-Indian resident.
Now, the Indian authorised dealers can provide loans to foreign people against the security of shares or immovable property in India. Also, the dealers and housing finance institutes can grant loans to NRIs as per the terms and conditions.
The proceeds must be realised within the 6 months of export. In case of export to foreign the proceeds must be realised within 15 months from the date of shipment. In FEMA provisions, another regulation has been made to provide powers to the dealers in terms of providing the extension of time.
1. A person who is resident in India on whom foreign exchange is due is obligated to take reasonable steps to realise foreign exchange through FEMA provisions act or regulations made under general or special permission of Reserve Bank.
2. Any settlement or gift to a person resident in India must be sold to an authorised person within a period of seven days of its receipt and in all other cases, within 90 days of its receipt.
3. Any person who has drawn the foreign exchange for some purpose but uses it for another purpose. So, under the FEMA provisions, the person must surrender the unutilised foreign exchange to an authorised person within the period of 60 days.
If any person will break the rules, provisions, order, or notification issued under the FEMA act, they will be liable to pay a penalty of thrice the amount included in such contravention or up to Rs. 2 lakhs. In case of the continuation of the contravention, then they are liable to pay the penalty with each extended day, amount Rs. 5 thousand for every single day.
the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has published the "List of non-bank AD Cat-II entities and FFMCs on which penalties have been imposed for contraventions of FEMA, 1999 - F.Y. 2024-25 (as on November 30, 2024). Check Here
At Registrationwala, FEMA Consultant can help you in the following ways:
Q1. What are the key features of FEMA Act 1999?
A. The key features of the Act include regulating forex transactions, dividing dealings into current/capital accounts and granting the RBI the power to oversee such transactions.
Q2. What are the objectives of FEMA Act?
A. FEMA’s objectives are to develop and regulate the forex market.
Q3. What is FEMA violation?
A. It refers to violations of any of the provisions of the FEMA Act. It can result in serious penalties and in some cases, cancellation of the FEMA license.
Q4. When was FEMA introduced?
A. It was introduced in 1999. However, it was enforced on 1 June, 2000.
Q5. What are the benefits of FEMA?
A. Benefits of FEMA include: (i) smooth flow of foreign funds, (ii) orderly development of the forex market, (iii) prevention of money laundering (iv) encouraging foreign investment.
Q6. What is the importance of FEMA?
A. FEMA regulates the foreign exchange market and ensures smooth and legal flow of foreign funds into India.

Hey there, I'm Dushyant Sharma. With the extensive knowledge I've gained in past 8 years, I have been creating content on various subjects such as banking, insurance, telecom, and all the important registration and licensing processes for various companies. I'm here to help everyone with my expertise in these areas through my articles.
Want to know More ?